How Much Electromagnetic Radiation Comes From A 2.4 GHz Cordless Phone? [Report]
 How far does the RF radiation from your DECT cordless phone reach inside your home and how strong is it. A real-life study performed by us with a DECT cordless phone provides us with some answers. The paper was presented at the EMF Workshop in Rhodes, Greece in 2002.
How far does the RF radiation from your DECT cordless phone reach inside your home and how strong is it. A real-life study performed by us with a DECT cordless phone provides us with some answers. The paper was presented at the EMF Workshop in Rhodes, Greece in 2002.
Abstract
The use of DECT (Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunication) cordless phones has been a major health and environmental concern in Europe and especially in Germany for years. The biological concern arose from studies on HF (high frequency) sources such as GSM cellular phones and towers. Digital cordless phones are also available in the USA – marketed as 2.4 GHz digital technology. A digital cordless phone was placed in a representative private home in California and HF measurements were conducted at different locations inside, using frequency selective spectrum analysis to obtain the cordless phone power densities. The results showed that the radiation patterns and levels emitted by the small cordless phone base station are almost identical to the DECT technology – also digitally pulsed and permanent microwave radiation. The power density values presented for each room inside the home can be compared to average DECT cordless phone radiation exposures found in German homes. The maximum power density was found to be over 500,000 µW/m2 at a normally encountered distance (about 1 – 2 feet) if the base station is placed on an office desk or bedside table. The radiation peak values in the same room are higher than those encountered in proximity to cellular base stations located near residential buildings.
Introduction
DECT cordless phones usage has been a major health and environmental concern in Europe and especially in Germany for years. Now multiple handsets cordless phones are also available in the USA – extolled as 2.4 GHz digital technology with multiple handsets following the DFHSS (Digital Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum) standard which is almost identical to DECT. The biological concern arose from studies on high frequency (HF) sources such as cellular phones and cellular phone base stations with GSM technology. The digital pulsed pattern of GSM and DECT radiation has come under suspicion to cause e.g. brain cancer, lymphoma, and changes in the brain blood barrier. The problem with the cordless DECT phones is, that the base station permanently emits full power pulsed microwave radiation, whether the phone is used or not. This creates constant exposure to high levels of the most critical type of HF radiation known throughout the entire home or office. The DECT technology is a European standard for cordless phones in the range of microwave radiation (1.8 to 1.9 Gigahertz, GHz). Identical permanently emitting portable phones with the special option of multiple handsets are available in the US and therefore the exposure issues are relevant for US population. In the US, the cordless phone manufacturers established the 2.4 GHz digital pulsed technology in the range of 2.4 – 2.5 GHz. Cordless phones such as e.g. the GIGASET (same name as a DECT cordless phone series by the same manufacturer in Germany) are available in USA.
Methods
A GIGASET cordless phone model was selected as a representative DFHSS 2.4 GHz phone for typical home and office usage. The base station was purchased in the US and placed on a wooden office desk in a representative 3 bedroom residential building in California. In the first test set, the power density in the room was measured prior to the activation of the base station to obtain background levels at the test site. Power density measurements were performed at different distances and directions from the phone (see table 1 and 2) with an Advantest R4131C spectrum analyzer (Rohde & Schwarz) and a calibrated periodic logarithmic log.per. antenna UKLP 9140-A (Schwarzbeck). The power density measurements were conducted under real-life conditions and only peak values (pulse maximum) were measured. All measurements were conducted following VDB guideline (VDB 2002) and the Swiss BUWAL guideline (BUWAL 2002). The power density levels are given in µW/m2 (microwatt per square meter). 1 µW/m2 equals 0.1 nW/cm2 (nanowatt per square centimeter). The background level was <0.3 µW/m2 (-58 dBm) in the range of all wireless, analogue or digital cordless, and cellular phone applications (0.3 to 3.5 GHz). See figure 1.
Results
High frequency measurements were conducted and showed that the radiation patterns and levels emitted by GIGASET 2.4 GHz cordless phone base station are identical to the DECT technology – also digitally pulsed with permanent microwave radiation. For comparison, the radiation levels from the GIGASET located in the same room are even higher than encountered in proximity (50 to 100 feet) to most cellular base station located on pole mount positions or on top of office buildings. However, in this case the source of the radiation is a desktop personal cordless phone.
| Figure 1: Spectrum analysis (no 2.4 GHz) | Figure 2: Spectrum analysis (with 2.4 GHz) |
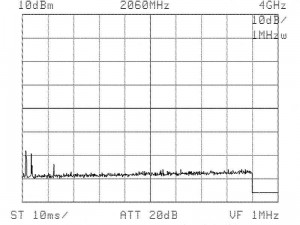 |
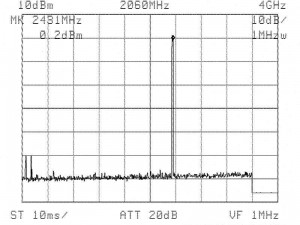 |
After the phone was plugged in, the radiation level rose to 673,000 µW/m2 (+0.2 dBm) in a normally encountered distance (about 1 – 2 feet) if the base station is placed on an office desk. See figure 2. The following power density levels were obtained :
Table 1: 2.4 GHz cordless phone base station power density levels in the same room
|
US GIGASET (2.4 GHz)* |
GERMANY GIGASET (DECT)** |
|
|
Distance |
DFHSS (Digital Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum) digital pulsed 100 Hz |
DECT (Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunication) digital pulsed 100 Hz |
|
30 centimeter – 12.5“ |
673,000 µW/m2 |
405,000 µW/m2 |
|
50 centimeter – 19.8” |
280,000 µW/m2 |
146,000 µW/m2 |
|
1 meter – 39.4” |
72,000 µW/m2 |
36,000 µW/m2 |
|
2 meter – 78.8“ |
23,000 µW/m2 |
9,100 µW/m2 |
*this study, **OEKO-TEST 1996
The results of the US GIGASET showed similar power densities when compared with the power densities reported for the GIGASET sold in Germany with DECT technology. Physical barriers such as e.g. wood framed walls, cabinets, closets have only a limited shielding effect inside a building. To evaluate a real life radiation exposure, the base station was placed on a desk in a bedroom (home office) and the actual power densities were measured in the different rooms. In this experimental test set, the real life effect of such a cordless phone installed in an average home and its associated radiation exposures were evaluated. The following values were obtained during our test set. The measurements showed a significant exposure for the occupants (see also table 2 and floor plan in appendix, figure 4)
Table 2: 2.4 GHz cordless phone base station power density levels in the house
|
Room |
Power Density (maximum pulse peak value) |
|
Office with phone |
33,800 µW/m2 |
|
Master bedroom |
13,500 µW/m2 |
|
Bedroom 2 |
5,400 µW/m2 |
|
Bedroom 3 |
680 µW/m2 |
|
Living room |
140 µW/m2 |
|
Family room |
50 µW/m2 |
|
Outside |
9 µW/m2 |
Besides the permanent emission from such a base station, the pulsed nature of the signal was analyzed and is displayed in figure 3. The spectrogram shows the periodic pulsed signal. The dynamic range of the power density covers the full range scale from minimum (pause) to maximum (pulse) and is sending out pulses every 10 milliseconds (ms) or 100 Hz (Hertz).
Figure 3: Pulsed signal of 2.4 GHz DFHSS technology – ZERO SPAN
(GIGASET cordless phone base station)
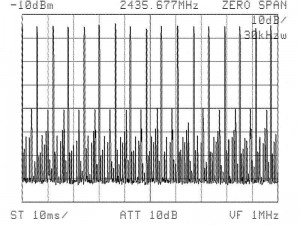
Summary
The levels encountered are considerably high for an indoor source, which emits permanently. The radiation peak values in the same room are higher than those encountered in proximity to cellular base stations located at pole mount or roof top positions. Even in the master bedroom and in the second bedroom, the power density levels were in the range of or above the 95. percentile radiation level just recently obtained from a study of cellular phone tower measurements in residential areas (HAUMANN 2002). For comparison, thermal (guidelines), other non-thermal (recommendations), and cellular tower exposure reference values are listed in the table 3 below.
Table 3: Comparison of Standard Threshold Values and Recommendations
|
Comparison of Standard Threshold Values and Recommendations |
Total Power Density |
|
Standards, > 2,000 MHz (e.g.) |
|
|
FCC/ANSI – USA |
10,000,000 µW/m2 |
|
Germany, England, Finland and Japan |
10,000,000 µW/m2 |
|
Belgium |
1,200,000 µW/m2 |
|
Switzerland and Italy |
90,000 µW/m2 |
|
Recommendations / References (e.g.) |
|
|
Ecolog Study, Germany (Ecolog 2000) |
10,000 µW/m2 |
|
Cellular tower radiation – high exposure level, 95. percentile (Haumann 2002) |
6,300 µW/m2 |
|
Salzburg, Austria (Resolution 2000) |
1,000 µW/m2 |
|
EU Parliament (STOA 2001) |
100 µW/m2 |
|
Cellular tower radiation – background level, 20. percentile (Haumann 2002) |
15 µW/m2 |
|
Low exposure, Oeko-Test (Oeko Test 2001) |
10 µW/m2 |
|
Nighttime exposure, Baubiology Standard (SBM 2000) |
0.1 µW/m2 |
|
Natural cosmic microwave radiation (Maes 2000) |
< 0.000001 µW/m2 |
Many European researcher, physicians, environmental professionals and toxicologist signed a resolution requesting the immediate stop of the DECT technology. This petition was delivered to the Germany Environmental Minister Mr. Jürgen Trittin in October of 1999 (Resolution 1999). The Germany magazine “Oeko-Test” (equivalent to the US magazine Consumer Test) had 16 DECT cordless phones tested, published the measurement results, and rated all phones as not recommendable due to the constant emission of high levels of pulsed radiation (Oeko-Test 1999).
Conclusions
As long as the only base for official standards on high frequency radiation are thermal effects and heating of the body tissue (FCC, ICNIRP, ANSI, IEEE, NCRP) there is no need for the industry to invest into saver products. More and more scientists state that the view of energy absorption only is insufficient to describe the possible effects on human health. Potential biological effects need to be considered due to
- Non-thermal or low intensity levels of HF radiation,
- Chronic versus acute exposure and,
- Pulsed HF radiation, which is reported to be more bioactive than constant wave HF radiation.
The human body reacts much more complex than acknowledged in the thermal model and is very sensitive to extreme periodic stimuli. The biological system takes the “energy” as well as the “information” which is brought e.g. by the continuous pulsed modulation pattern.
Much experimental evidence of non-thermal influences of microwave radiation on living systems has been published in the scientific literature during the last 30 years – relating both to in vitro and in vivo studies – and were reviewed just recently by the STOA commission of the European Parliament (STOA 2001). From the use of microwave wireless technologies e.g. the following non-thermal biological effects have been reported:
- Changes in the electrical activity in the human brain,
-
Increase in DNA single and double strand breaks from HF exposure to 2.45 GHz,
-
Increased lymphoma rates (2 fold) in transgenic mice exposed twice a day exposed to 30 minutes of cell phone (GSM) signals over 18 month,
-
Increased permeability of the blood-brain barrier in rats,
-
Observation of an increase in resting blood pressure during exposure,
-
Increased permeability of the erythrocyte membrane,
-
Effects on brain electrochemistry (calcium efflux),
-
Increase of chromosome aberrations and micronuclei in human blood lymphocytes,
-
Synergistic effects with cancer promoting and certain psychoactive drugs,
-
Depression of chicken immune systems,
-
Increase in chicken embryo mortality,
-
Effects on brain dopamine/opiate electrochemistry,
-
Increases in DNA single and double strand breaks in rat brain,
-
Stressful effects in healthy and tumor bearing mice,
-
Neurogenetic effects and micronuclei formation in peritoneal macrophage.
In this review study, a threshold of 1000 µW/m2 was evaluated for non-thermal biological effects. For locations with any long-term exposure, a further safety factor of 10 was recommended for pulsed cellular phone radiation sources as cellular phone base stations. In this case, the power densities should not exceed 100 µW/m2.
The constant High-Tec HF radiation brought into the US homes and offices by 2.4 GHz digital technology cordless phones is definitely a big step in the wrong direction in terms of environmental health protection and radiation exposure prevention. This reveals a complete misunderstanding of progress for our new millennium.
Read Additional EMF RF Articles:
- RF Radiation Study: How To Measure RF Exposure
- Is An iPad Radiation Shield For RF Shielding Effective?
- Cell Tower Shielding In San Diego
If you would like to learn more about detection and shielding of electromagnetic radiation exposure from cordless phones or other devices, call the experts at EMFRF Solutions to have your location tested and advice on how to properly shield from EMF or RF radiation. Call 760-942-9400 Today!
References
BUWAL 2002 Schweizer Messvorschrift für GSM-Sender 2002, BUWAL – Bundesamt für Umwelt, Wald und Landschaft. (www.buwal.ch)
Ecolog 2000 Hennies K., Neitzke H.-P. & Voigt H., Mobilfunk und Gesundheit – Bewertung des wissenschaftlichen Erkenntnisstandes unter dem Gesichtspunkt des vorsorgenden Gesundheitsschutzes. Im Auftrag der T-Mobil. Hannover, April 2000 (ECOLOG-Institut für sozial-ökologische Forschung und Bildung, Nieschlagstr. 26, D-30449 Hannover, Germany)
Haumann 2002 Haumann Th., Sierck P., Maes W. and Münzenberg U., HF-Radiation of GSM Cellular Phone Towers in Residential Areas, in Biological Effects of Electromagnetic Fields 2nd International Workshop Rhodes, Greece / 7 – 11 October 2002 (submitted for presentation)
MAES 2000 Maes W., Stress durch Strom und Strahlung, 4. Ed. 2000, Verlag Institut für Baubiologie und Oekologie IBN, Neubeuern, Germany.
Oeko-Test 1996 Test “Schnurlose Telefone”, Öko-Test 3/1996 Germany, Maerz 1996. (www.oekotest.de)
Oeko-Test 1999 Test “Schnurlose Telefone”, Öko-Test 11/1999 Germany, November 1999.
Oeko-Test 2001 Test “Mobilfunk-Sendeanlagen”, Öko-Test 4/2001 Germany, April 2001, pp. 32 – 40.
Resolution 1999 Resolution for Bundesumweltminister Trittin, Germany, delivered on 19.10.1999 during the event “Buergerforum Elektrosmog” organized from the Bundesministerium für Umwelt, Naturschutz und Reaktorsicherheit in Bonn, Germany.
Resolution 2000 Salzburg Resolution on Mobile Telecommunication Base Stations – International Conference on Cell Tower Siting, Linking Science & Public Health, Salzburg, Austria, June 7-8, 2000. (www.land-sbg.gv.at/celltower)
SBM 2000 Baubiologie Maes and IBN, Standard der Baubiologischen Messtechnik SBM 2000, Richtwerte für Schlafbereiche, in “Stress durch Strom und Strahlung”, Maes W., 4th Ed. 2000, pp. 542 – 545, Verlag Institut für Baubiologie und Oekologie IBN, Neubeuern, Germany.
STOA 2001 THE PHYSIOLOGICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL EFFECTS OF NON-IONISING ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION, STOA – Scientific and Technological Options Assessment, Options Brief and Executive Summary, PE Nr. 297.574 March 2001, (www.europarl.eu.int)
VDB 2002 VDB-Richtlinie, Teil II A 3, draft 2002, Verband Deutscher Baubiologen e.V. (www.baubiologie.net)
Appendix
Figure 4: Floor plan with exposure data
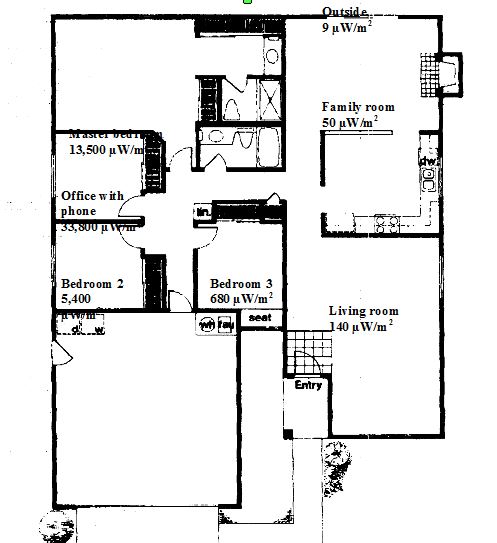
Figure 4: Floor plan with exposure data
Nonstop Pulsed 2.4 GHz Radiation Inside US Homes
Thomas Haumann1 and Peter Sierck2
1Umweltanalytik und Baubiologie,
Meisenburgstrasse 25, D-45133 Essen, Germany
2Environmental Testing & Technology, Inc.,
1106 Second Street, Encinitas CA 92024, USA

